qPCR data
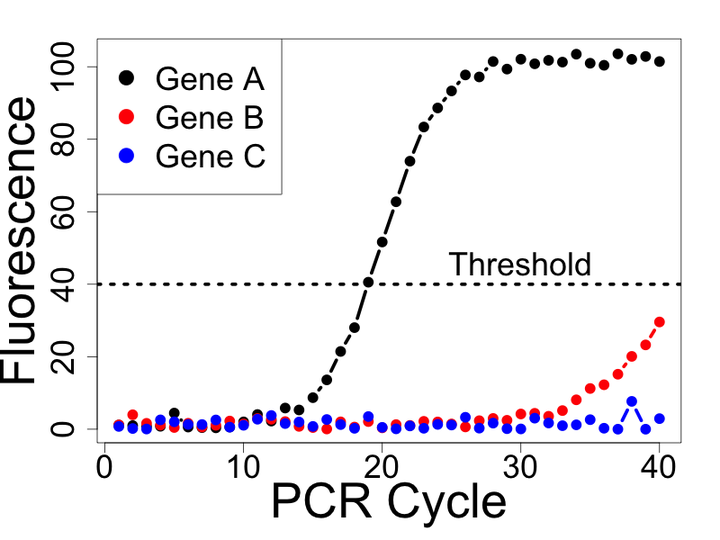
Quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) remains one of the most widely used methods to quantify gene expression. Unlike other genomic technologies, qPCR allows one to measure the rate of amplification across PCR cycles. Analysis of the resulting amplification data can be used to estimate a quantity proportional to the initial amount of the target molecule in a sample. My research group has focused on two areas of methodological development related to the analysis of qPCR data. First, we demonstrated that previous methods of handling non-detects, reactions failing to produce an expression estimate, often introduce substantial bias in estimates of differential gene expression. Specifically, we demonstrated that non-detects likely represent a specific type of missing data, called missing not at random, and developed several methods to appropriately model and account for this type of missing data. Second, we demonstrated that current methods of model-based expression estimation from qPCR amplification data introduce systematic biases and that smooth transition auto-regressive models are able to better capture the amplifcation process.